A) $380 billion;125
B) $500 billion;150
C) $500 billion;100
D) $620 billion;125
E) $500 billion;125
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In new classical cycle theory,________ bring fluctuations in real GDP around potential GDP.
A) unexpected changes in aggregate demand
B) expected changes in aggregate demand
C) fluctuations in money growth with rigid wages
D) fluctuations in investment coupled with rigid wages
E) expected changes in labour productivity
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following question.
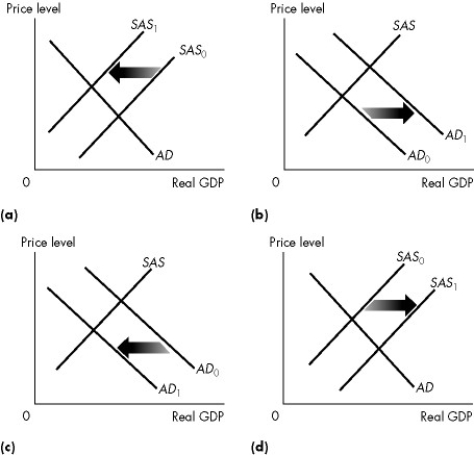 Figure 28.1.5
-The economy starts out at a full-employment equilibrium.Some events then occur that generate a demand-pull inflation.
All of the following events except an increase in ________ might cause a demand-pull inflation.
Figure 28.1.5
-The economy starts out at a full-employment equilibrium.Some events then occur that generate a demand-pull inflation.
All of the following events except an increase in ________ might cause a demand-pull inflation.
A) the money wage rate
B) exports
C) the quantity of money
D) government expenditure
E) transfer payments
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A movement down along the short-run Phillips curve results from an unanticipated
A) decrease in aggregate demand.
B) increase in aggregate demand.
C) decrease in short-run aggregate supply.
D) increase in short-run aggregate supply.
E) increase in the natural unemployment rate.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
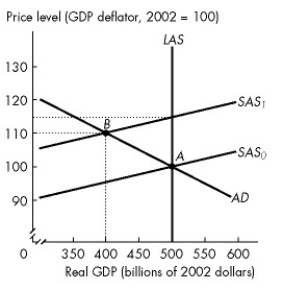 Figure 28.1.2
-Refer to Figure 28.1.2.If SAS shifts from SAS? to SAS?,then
Figure 28.1.2
-Refer to Figure 28.1.2.If SAS shifts from SAS? to SAS?,then
A) inflation is expected to be 10 percent.
B) inflation will be 10 percent.
C) a recession will occur.
D) unemployment will fall.
E) B and C.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Along the short-run Phillips curve,everything remaining the same,the higher the
A) unemployment rate, the lower the inflation rate.
B) price level, the lower the inflation rate.
C) money wage rate, the lower is the unemployment rate.
D) quantity of money, the lower the unemployment rate.
E) growth rate of the quantity of money, the higher the inflation rate.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which business cycle theory emphasizes that,because of previously negotiated wage agreements,both expected and unexpected fluctuations in aggregate demand can change real GDP?
A) the new classical cycle theory
B) the new Keynesian cycle theory
C) Monetarist cycle theory
D) Keynesian cycle theory
E) Real business cycle theory
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ states that the main source of economic fluctuations is fluctuations in business confidence.
A) Real business cycle theory
B) New classical cycle theory
C) Keynesian cycle theory
D) Monetarist cycle theory
E) None of the above
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose aggregate demand increases by more than expected.Which of the following describes what occurs?
A) Real GDP is greater than potential GDP.
B) The price level rises.
C) Unemployment falls.
D) The natural unemployment rate does not change.
E) All of the above.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the short-run Phillips curve in Canada since the 1960s. Choose the best statement.
A) Canada's inflation/unemployment tradeoff is best shown as a series of shifting short-run Phillips curves that sometimes shift upward and sometimes shift downward.
B) Canada's inflation/unemployment tradeoff is undefined.
C) Canada's short-run Phillips curve is consistently shifting upward.
D) Canada's short-run Phillips curve is consistently shifting downward.
E) Canada's short-run Phillips curve is consistently shifting rightward.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The economy starts out at a full-employment equilibrium.Some events then occur that generate a cost-push inflation. Which of the following events might cause a cost-push inflation?
A) a decrease in exports
B) an increase in the quantity of money
C) a decrease in government expenditure
D) an increase in the money wage rate or an increase in the money prices of raw materials
E) an increase in taxes
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Stagflation is the result of
A) a decrease in aggregate demand.
B) a decrease in short-run aggregate supply.
C) an increase in aggregate demand.
D) an increase in short-run aggregate supply.
E) a decrease in short-run aggregate supply combined with a simultaneous increase in aggregate supply.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the real business cycle theory,during a recession the demand for labour ________ and the supply of labour ________.
A) increases;decreases
B) decreases;does not change
C) does not change;decreases
D) decreases;decreases
E) decreases;increases
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Canadian long-run Phillips curve ________ when the expected inflation rate rises and ________ when the expected inflation rate falls. The Canadian long-run Phillips curve ________ when the natural unemployment rate increases and ________ when the natural unemployment rate decreases.
A) does not shift;does not shift;does not shift;does not shift
B) does not shift;does not shift;shifts rightward;shifts leftward
C) shifts upward;shifts downward;shifts rightward;shifts leftward
D) shifts rightward;shifts leftward;does not shift;does not shift
E) shifts rightward;shifts leftward;shifts rightward;shifts leftward
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 28.1.2
-Refer to Figure 28.1.2.The economy is in long-run equilibrium.If the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward from SAS? to SAS?,ceteris paribus,then the actual inflation rate
Figure 28.1.2
-Refer to Figure 28.1.2.The economy is in long-run equilibrium.If the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward from SAS? to SAS?,ceteris paribus,then the actual inflation rate
A) is greater than the expected inflation rate.
B) is less than the expected inflation rate.
C) is the same as the expected inflation rate.
D) cannot be determined without more information.
E) depends on what happens to wage settlements.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 28.1.2
-Refer to Figure 28.1.2.The vertical distance between SAS? and SAS? represents the
Figure 28.1.2
-Refer to Figure 28.1.2.The vertical distance between SAS? and SAS? represents the
A) actual inflation rate.
B) expected increase in real GDP.
C) actual decrease in real GDP.
D) expected inflation rate.
E) expected decrease in the real wage rate.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following can create a demand-pull inflation?
A) a sharp increase in the price of oil
B) higher wages negotiated by unions
C) a cut in the interest rate
D) a decrease in investment as a result of a decrease in expected future profits
E) a decrease in government expenditure on goods and services
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following question.
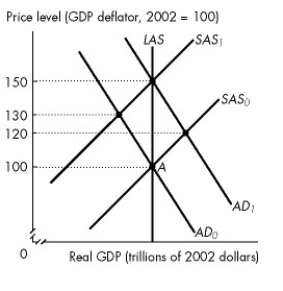 Figure 28.1.4
-Refer to Figure 28.1.4.The figure illustrates an economy initially in equilibrium at point A.If the quantity of money is expected to increase by 50 percent,what is the rational expectation of the price level?
Figure 28.1.4
-Refer to Figure 28.1.4.The figure illustrates an economy initially in equilibrium at point A.If the quantity of money is expected to increase by 50 percent,what is the rational expectation of the price level?
A) 100
B) 120
C) 130
D) 150
E) We cannot tell without more information on wage negotiations.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 28.2.2
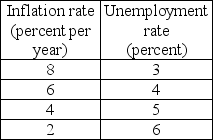 -Refer to Table 28.2.2.The economy's natural unemployment rate is 4 percent.Table 28.2.2 gives some points on the economy's short-run Phillips curve.When the unemployment rate is 4 percent ________.
-Refer to Table 28.2.2.The economy's natural unemployment rate is 4 percent.Table 28.2.2 gives some points on the economy's short-run Phillips curve.When the unemployment rate is 4 percent ________.
A) actual inflation is greater than expected inflation
B) actual inflation is less than expected inflation
C) and the inflation rate is 6 percent a year, the short-run and long-run Phillips curves intersect
D) and the expected inflation rate is 8 percent a year, the short-run Phillips curve shifts downward
E) aggregate demand increases
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to real business cycle theory,workers' decisions to work now versus later depend on
A) the real wage rate today but not the real wage rate in the future.
B) the money wage rate.
C) the real interest rate.
D) labour productivity.
E) none of the above.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 101
Related Exams