A) a nucleotide-pair substitution
B) a deletion of three nucleotides near the middle of a gene
C) a single nucleotide deletion in the middle of an intron
D) a single nucleotide deletion near the end of the coding sequence
E) a single nucleotide insertion downstream of, and close to, the start of the coding sequence
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following variations on translation would be most disadvantageous for a cell?
A) translating polypeptides directly from DNA
B) using fewer kinds of tRNA
C) having only one stop codon
D) lengthening the half-life of mRNA
E) having a second codon (besides AUG) as a start codon
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In eukaryotic cells, transcription cannot begin until
A) the two DNA strands have completely separated and exposed the promoter.
B) several transcription factors have bound to the promoter.
C) the 5' caps are removed from the mRNA.
D) the DNA introns are removed from the template.
E) DNA nucleases have isolated the transcription unit.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Garrod hypothesized that "inborn errors of metabolism" such as alkaptonuria occur because
A) metabolic enzymes require vitamin cofactors, and affected individuals have significant nutritional deficiencies.
B) enzymes are made of DNA, and affected individuals lack DNA polymerase.
C) many metabolic enzymes use DNA as a cofactor, and affected individuals have mutations that prevent their enzymes from interacting efficiently with DNA.
D) certain metabolic reactions are carried out by ribozymes, and affected individuals lack key splicing factors.
E) genes dictate the production of specific enzymes, and affected individuals have genetic defects that cause them to lack certain enzymes.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A part of the promoter, called the TATA box, is said to be highly conserved in evolution. Which of the following might this illustrate?
A) The sequence evolves very rapidly.
B) The sequence does not mutate.
C) Any mutation in the sequence is selected against.
D) The sequence is found in many but not all promoters.
E) The sequence is transcribed at the start of every gene.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An experimenter has altered the 3' end of the tRNA corresponding to the amino acid methionine in such a way as to remove the 3' AC. Which of the following hypotheses describes the most likely result?
A) tRNA will not form a cloverleaf.
B) The nearby stem end will pair improperly.
C) The amino acid methionine will not bind.
D) The anticodon will not bind with the mRNA codon.
E) The aminoacylsynthetase will not be formed.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not true of RNA processing?
A) Exons are cut out before mRNA leaves the nucleus.
B) Nucleotides may be added at both ends of the RNA.
C) Ribozymes may function in RNA splicing.
D) RNA splicing can be catalyzed by spliceosomes.
E) A primary transcript is often much longer than the final RNA molecule that leaves the nucleus.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the next few questions. The enzyme polynucleotide phosphorylase randomly assembles nucleotides into a polynucleotide polymer. -You add polynucleotide phosphorylase to a solution of ATP, GTP, and UTP. How many artificial mRNA 3 nucleotide codons would be possible?
A) 3
B) 6
C) 9
D) 27
E) 81
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions refer to this figure of a simple metabolic pathway:
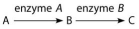 -If A, B, and C are all required for growth, a strain mutant for the gene-encoding enzyme B would be capable of growing on which of the following media?
-If A, B, and C are all required for growth, a strain mutant for the gene-encoding enzyme B would be capable of growing on which of the following media?
A) minimal medium
B) minimal medium supplemented with A only
C) minimal medium supplemented with B only
D) minimal medium supplemented with C only
E) minimal medium supplemented with nutrients A and B
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following model of a eukaryotic transcript to answer the next few questions. 5' UTR E₁ I₁ E₂ I₂ E₃ I₃ E₄ UTR 3' -Which components of the previous molecule will also be found in mRNA in the cytosol?
A) 5' UTR I₁ I₂ I₃ UTR 3'
B) 5' E₁ E₂ E₃ E₄ 3'
C) 5' UTR E₁ E₂ E₃ E₄ UTR 3'
D) 5' I₁ I₂ I₃ 3'
E) 5' E�₁ I₁ E₂ I₂ E₃ I₃ E₄ 3'
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use this representation to answer the following questions. DNA template strand 5' ____________________________ 3' DNA complementary strand 3' ____________________________ 5' -In the transcription event of the previous DNA, where would the promoter be located?
A) at the 3' end of the newly made RNA
B) to the right of the template strand
C) to the left of the template strand
D) to the right of the sense strand
E) to the left of the sense strand
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which component is not directly involved in translation?
A) mRNA
B) DNA
C) tRNA
D) ribosomes
E) GTP
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following mutations is most likely to cause a phenotypic change?
A) a duplication of all or most introns
B) a large inversion whose ends are each in intergenic regions
C) a nucleotide substitution in an exon coding for a transmembrane domain
D) a single nucleotide deletion in an exon coding for an active site
E) a frameshift mutation one codon away from the 3' end of the nontemplate strand
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the function of GTP in translation?
A) GTP energizes the formation of the initiation complex, using initiation factors.
B) GTP hydrolyzes to provide phosphate groups for tRNA binding.
C) GTP hydrolyzes to provide energy for making peptide bonds.
D) GTP supplies phosphates and energy to make ATP from ADP.
E) GTP separates the small and large subunits of the ribosome at the stop codon.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions refer to this table of codons.
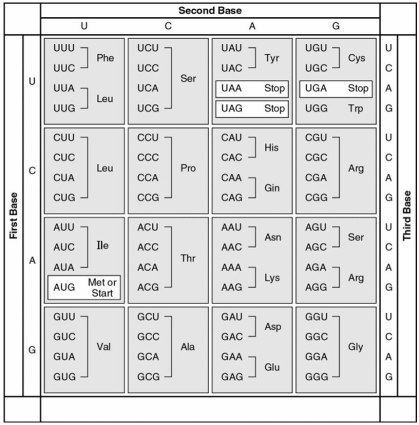 -What amino acid sequence will be generated, based on the following mRNA codon sequence? 5' AUG-UCU-UCG-UUA-UCC-UUG 3'
-What amino acid sequence will be generated, based on the following mRNA codon sequence? 5' AUG-UCU-UCG-UUA-UCC-UUG 3'
A) met-arg-glu-arg-glu-arg
B) met-glu-arg-arg-glu-leu
C) met-ser-leu-ser-leu-ser
D) met-ser-ser-leu-ser-leu
E) met-leu-phe-arg-glu-glu
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true about protein synthesis in prokaryotes?
A) Extensive RNA processing is required before prokaryotic transcripts can be translated.
B) Translation can begin while transcription is still in progress.
C) Prokaryotic cells have complicated mechanisms for targeting proteins to the appropriate cellular organelles.
D) Translation requires antibiotic activity.
E) Unlike eukaryotes, prokaryotes require no initiation or elongation factors.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that a mutation alters the formation of a tRNA such that it still attaches to the same amino acid (phe) but its anticodon loop has the sequence AAU that binds to the mRNA codon UUA (that usually specifies leucine leu) .
A) The modified tRNA will cause this mRNA to make only nonfunctioning product.
B) The tRNA-leu will not be able to enter the site of the ribosome to bind to the UUA.
C) One mutated tRNA molecule will be relatively inconsequential because it will compete with many "normal" ones.
D) The tRNA will be so unstable that it will not participate in translation.
E) The mutated tRNA will result in an amino acid variant in all copies of the protein.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the function of the release factor (RF) ?
A) It separates tRNA in the A site from the growing polypeptide.
B) It binds to the stop codon in the A site in place of a tRNA.
C) It releases the amino acid from its tRNA to allow the amino acid to form a peptide bond.
D) It supplies a source of energy for termination of translation.
E) It releases the ribosome from the ER to allow polypeptides into the cytosol.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the structural organization of many eukaryotic genes, individual exons may be related to which of the following?
A) the sequence of the intron that immediately precedes each exon
B) the number of polypeptides making up the functional protein
C) the various domains of the polypeptide product
D) the number of restriction enzyme cutting sites
E) the number of start sites for transcription
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following DNA mutations is the most likely to be damaging to the protein it specifies?
A) a base-pair deletion
B) a codon substitution
C) a substitution in the last base of a codon
D) a codon deletion
E) a point mutation
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 91
Related Exams